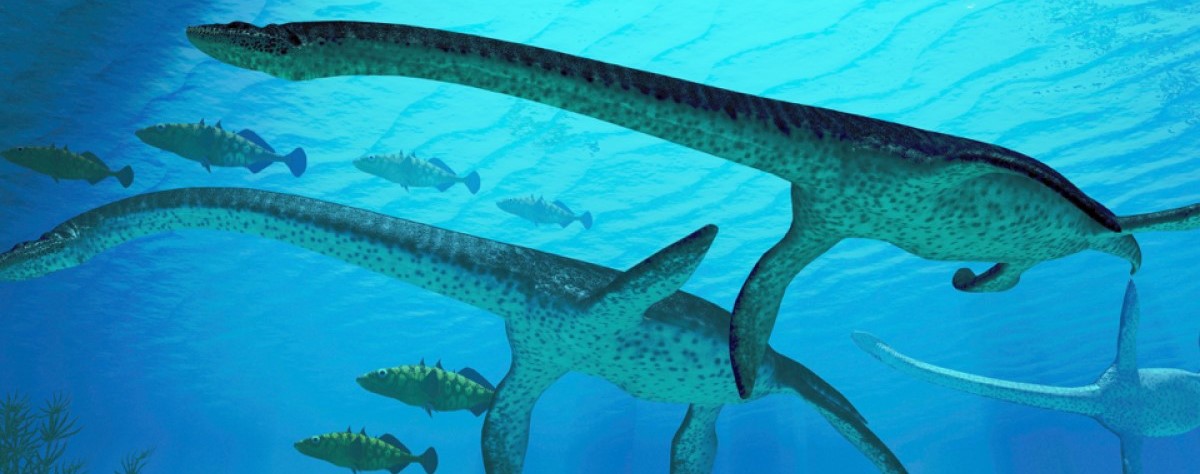
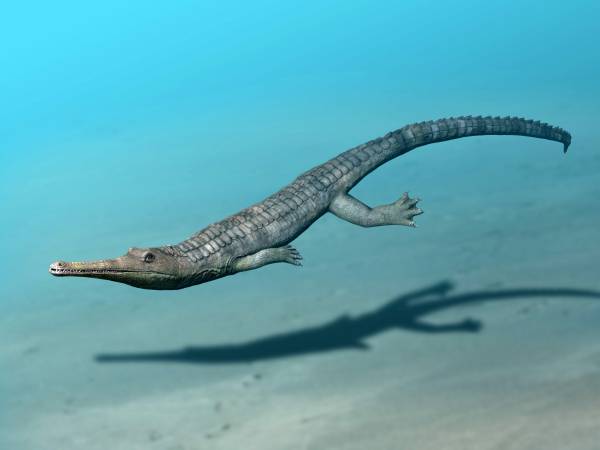
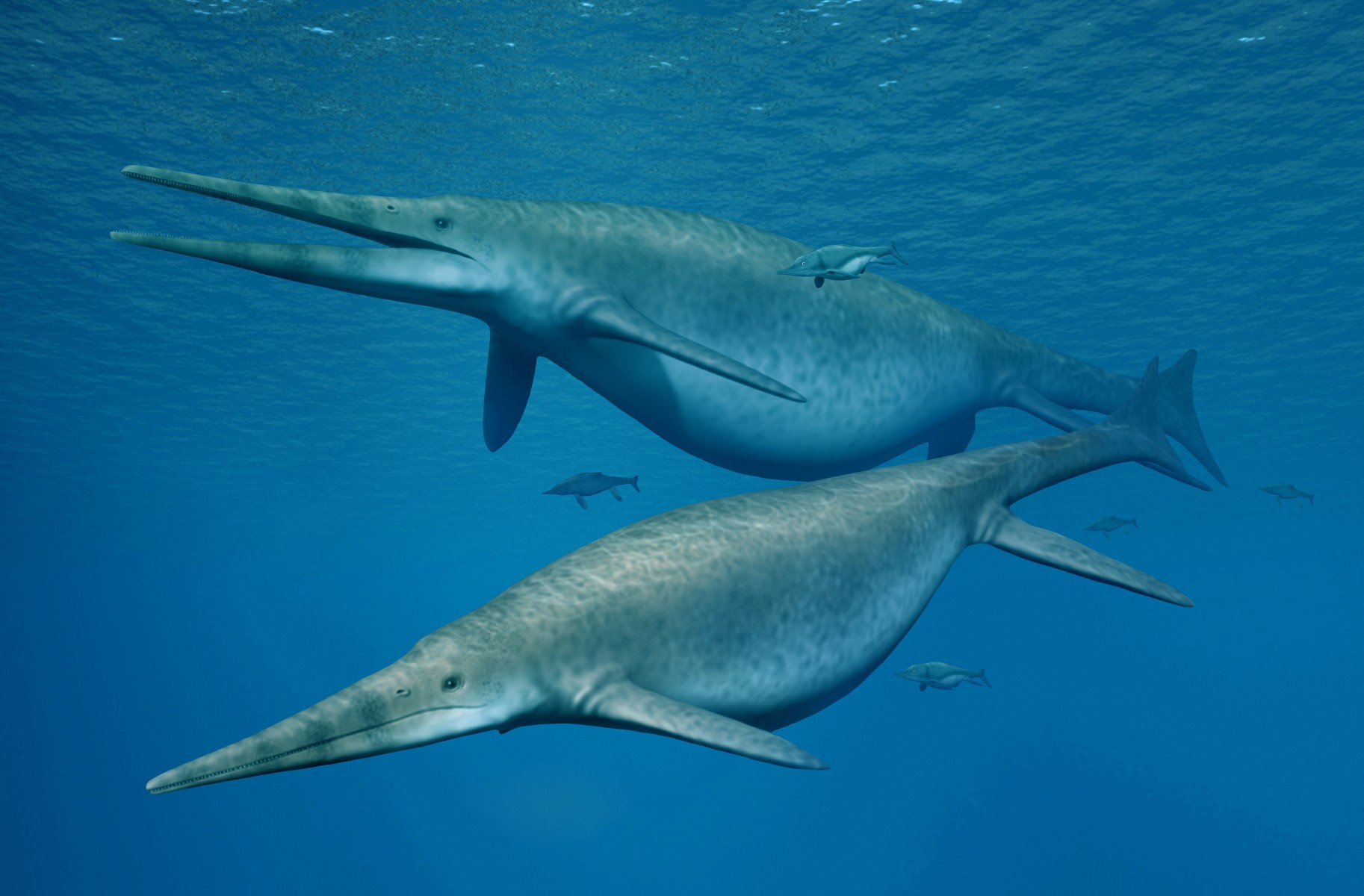
Ichthyosaurus
dolphin-like reptile lived during the Triassic and Jurassic periods. Anatomical features demonstrate that it was a visually-oriented predator; it had huge, sensitive eyes, protected by bony shields. Coprolites of Ichthyosaurus reveal that its diet consisted of fish and squid. Ichthyosaurus was smaller than most of its relatives, with individuals measuring up to 11 ft (3.3 m) in length.